10 Key Quantum Computing Breakthroughs in 2025
2025 has been a transformative year for quantum computing, with major advancements across hardware, error correction, AI integration, and quantum networks. Here's a quick summary of the most important breakthroughs shaping the future:
- Microsoft's Eight-Qubit Processor: A topological qubit design with only 1% error rates, paving the way for scalable quantum chips.
- IBM's 4,158-Qubit System: Combines quantum and classical computing for industries like finance, manufacturing, and telecommunications.
- Google's Neutral-Atom Quantum System: Achieves 99.5% fidelity with rubidium atoms, offering better scalability and energy efficiency.
- New Error Correction Methods: AWS's Ocelot chip reduces error correction costs by 90%, while Quantinuum achieves 22x better error rates with logical qubits.
- Quantum-AI Synergy: Quantum computing boosts AI efficiency by up to 1,000x while using significantly less energy.
- First Quantum Network: Caltech connects quantum nodes with entanglement multiplexing, enabling secure quantum communication.
- Chemical Modeling: Quantum systems improve molecular simulations, reducing computational costs by 1,000x and speeding up drug discovery.
- Quantum-Ready Security: Post-quantum cryptography gains traction, with 75% of encryption methods still vulnerable to quantum attacks.
- Advances in Quantum Measurement: New techniques enhance precision in healthcare, defense, and molecular detection.
- Public Access to Quantum Systems: Cloud platforms like Amazon Braket, IBM Qiskit, and Azure Quantum democratize access to quantum computing.
Quick Comparison of Key Developments
Area | Key Innovation | Impact |
|---|---|---|
Hardware | Microsoft's Eight-Qubit Processor | Scalable, low-error quantum chips |
Hybrid Systems | IBM's 4,158-Qubit System | Solves complex industry-specific problems |
New Technologies | Google's Neutral-Atom Quantum System | High fidelity, energy-efficient qubits |
Error Correction | AWS Ocelot Chip | Reduces costs by 90% |
AI Integration | Quantum-AI Hybrid Systems | 1,000x AI efficiency improvement |
Networking | Caltech's Quantum Network | Secure multi-qubit communication |
Chemical Modeling | HiVQE Algorithm | Faster, cheaper molecular simulations |
Security | Post-Quantum Cryptography | Protects against future quantum threats |
Measurement | Quantum Sensing with Diamonds | Precision in healthcare and defense |
Accessibility | Quantum Cloud Platforms | Democratizes quantum computing access |
These breakthroughs are redefining quantum computing's role in industries like healthcare, finance, and logistics while addressing challenges like error correction and security. Dive into the details to explore how these advancements are shaping the future.
Quantum Computing 2024 Update
1. Microsoft's Eight-Qubit Processor Design
Microsoft's Majorana 1 chip marks a leap forward in quantum computing. Introduced in early 2025, this processor features Microsoft's new Topological Core architecture, built with eight topological qubits [4][5]. At its core is a specialized topoconductor that manipulates Majorana particles - quasi-particles acting like "half-electrons" known for their strong resistance to errors [8]. This design addresses key scalability challenges in quantum computing.
"We took a step back and said 'OK, let's invent the transistor for the quantum age. What properties does it need to have?' And that's really how we got here – it's the particular combination, the quality and the important details in our new materials stack that have enabled a new kind of qubit and ultimately our entire architecture." – Chetan Nayak, Microsoft technical fellow [5]
The Majorana 1 processor achieves an error rate of just 1%, thanks to its compact qubit layout using aluminum nanowires arranged in an H-shaped pattern [5][7]. By using simple digital pulses instead of complex analog controls, Microsoft has managed to cut down error correction overhead by about ten times compared to older methods [6].
The chip's stability is impressive, with state changes occurring only once every millisecond on average [6]. Unlike other quantum systems that require networking multiple processors, Microsoft's approach focuses on scaling up to one million qubits on a single chip [4][7]. This ambitious design opens the door to groundbreaking applications, such as breaking down microplastics or creating self-healing materials for use in construction and healthcare [4].
2. IBM's Quantum-Based Computing System
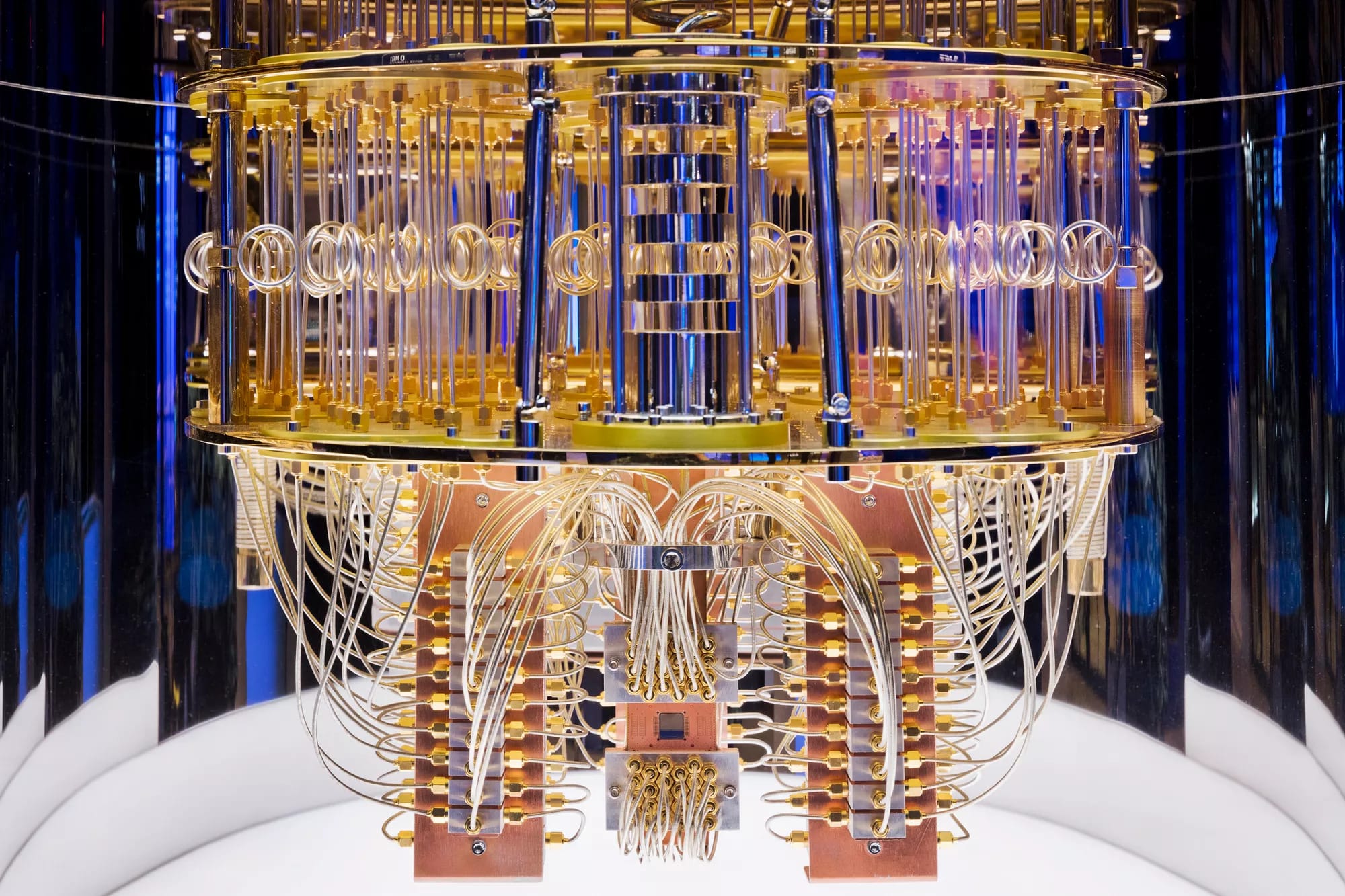
IBM's 'Kookaburra' processor is a major step forward in quantum computing. This 1,386-qubit multi-chip processor uses a quantum communication link to connect three chips, creating a powerful 4,158-qubit system [9].
IBM's system combines quantum processors with classical CPUs and GPUs, creating a hybrid setup that can solve problems beyond the reach of traditional computing [9]. Developers can leverage IBM's Quantum Serverless platform to seamlessly integrate quantum and classical resources, eliminating the need for deep hardware knowledge.
"The quantum-centric supercomputer will incorporate quantum processors, classical processors, quantum communication networks, and classical networks, all working together to completely transform how we compute." - IBM [9]
IBM's technology is already delivering results across industries:
Industry | Result | Impact |
|---|---|---|
Financial Services | Optimized option pricing | Reduced sample size from millions to thousands [11] |
Retail | Employee scheduling (Pattison Food Group) | 80% less scheduling effort [12] |
Manufacturing | Production scheduling (Ford Otosan) | 83% faster schedule creation [12] |
Telecommunications | Network optimization (NTT DOCOMO) | 15% better network performance [12] |
The system uses a circuit knitting technique to break down complex circuits into smaller parts that run on quantum hardware, then reassembles them using classical computing [9]. This method has already achieved impressive outcomes, like a 120x speedup in molecule simulation through Qiskit Runtime [9].
Dr. Stefan Woerner, an IBM mathematician, explains how this system improves financial modeling:
"This quantum algorithm can achieve a quadratic speed up, meaning that it needs significantly fewer samples - so while for the classical Monte Carlo simulation you need millions of samples, for quantum you only need a few thousand." [11]
This technology is reshaping computing, with applications in drug discovery, climate modeling, and artificial intelligence [13]. Thanks to its serverless architecture, IBM's quantum-centric supercomputer remains accessible to a wide range of users [9].
3. Google's Atom‑Based Quantum Computer
Google has introduced a new approach to quantum computing, moving from superconducting systems to neutral‑atom technology. This method uses individual laser‑cooled neutral atoms as qubits, controlled with optical tweezers. Unlike superconducting systems that require temperatures near absolute zero, Google's system operates at just a few microkelvins [17].
Here's a quick comparison of different quantum computing methods:
Feature | Neutral Atoms | Superconducting | Trapped Ions |
|---|---|---|---|
Scalability | High (2D grid setup) | Limited by wiring | Limited (1D setup) |
Coherence Time | 12.6 seconds | Milliseconds | Seconds |
Error Rate | 0.5% with 48 qubits | Variable | ~1% |
Temperature Needs | Few microkelvins | Near absolute zero | Ultra‑low |
Connectivity | All‑to‑all | Limited | Linear |
Dr. Mukund Vengalattore from DARPA highlights the precision of neutral‑atom systems:
"Every atom of rubidium is identical to every other item of rubidium in the universe. There are no fabrication imperfections, there are no errors in how you compose a rubidium atom – nature does that for us at a level that we can't even imagine. So when we trap these atoms, and we control them, and we measure their properties, we know that every rubidium atom in a certain sense acts exactly as every other rubidium atom." [17]
Caltech has demonstrated the potential of this technology by creating an array of 6,100 neutral cesium atoms, achieving a coherence time of 12.6 seconds and a two‑qubit fidelity of 99.5% [15][16].
Stuart Adams, a physicist at Durham University, explains the advantages of the Rydberg system:
"The Rydberg system offers you all this ability to shuffle qubits around and decide who's interacting with who, which gives you a flexibility that superconducting qubits don't have." [15]
Neutral‑atom quantum computers also consume far less energy than high‑performance computers (HPC), making them a more energy-efficient and cost-effective choice for large-scale applications [14].
Andrew Steane from the University of Oxford underscores the competitiveness of neutral‑atom technology:
"The combination of high‑fidelity gates, the large numbers of qubits, high‑accuracy measurements and flexible connectivity allows us to deem the Rydberg‑atom array as a real competitor to the superconducting and trapped‑ion qubits." [15]
4. New Error Correction Methods
Quantum error correction (QEC) made major strides in 2025, with Microsoft and Quantinuum setting the pace. Their partnership showcased 12 logical qubits on Quantinuum's 56-qubit trapped ion computer, achieving an error rate of 0.0011 - a 22x improvement compared to the physical qubits' error rate of 0.024 [18]. Building on this progress, companies are rolling out advanced hardware solutions to tackle errors more effectively.
Amazon Web Services (AWS) introduced the Ocelot chip in February 2025, slashing error correction costs by up to 90%. This chip features a scalable design that uses "cat qubits", which naturally minimize certain error types [22].
"We didn't take an existing architecture and then try to incorporate error correction afterwards. We selected our qubit and architecture with quantum error correction as the top requirement. We believe that if we're going to make practical quantum computers, quantum error correction needs to come first." – Oskar Painter, AWS Director of Quantum Hardware [22]
Meanwhile, researchers from the University of Innsbruck, RWTH Aachen, and Forschungszentrum Jülich developed a method allowing quantum systems to switch between two error correction codes. This approach ensures broader error protection [19].
"In this way, the quantum computer can switch to the second code whenever a logic gate that is difficult to realize appears in the first code. This makes it easier to implement all the gates required for computing." – Friederike Butt [19]
Here's a quick comparison of recent advancements in error correction:
Organization | Achievement | Error Rate | Factor |
|---|---|---|---|
Microsoft/Quantinuum | 12 logical qubits | 0.0011 | 22x improvement |
AWS (Ocelot Chip) | Cat qubit system | N/A | Up to 90% cost reduction |
UNSW Sydney | 8-state qudit system | N/A | High-dimensional states |
The ultimate goal for the industry is to build physical systems with a million qubits, capable of delivering around 100 reliable qubits and executing circuit depths of 10,000 [2]. Current methods rely on syndrome measurements to detect errors while preserving quantum information [21]. When paired with surface codes for 2D solid-state hardware, this approach strengthens the foundation for practical quantum computing [20].
These advancements are paving the way for more reliable quantum systems, bringing us closer to realizing their full potential.
5. Combined Quantum and AI Systems
Thanks to advancements in hardware and error correction, quantum computing is now merging with AI to tackle industrial challenges in new ways. By 2025, this combination led to impressive gains in efficiency and energy use.
In Italy, Quantinuum partnered with HPE Group to create a quantum-AI hybrid system. This system improved automotive battery design and aerodynamics. Another collaboration with Amgen used Parameterized Quantum Circuits on the H1 model to enhance peptide classification.
"We are at one of those moments where the hypothetical is becoming real and the breakthroughs made possible by the precision of this quantum-generated data will create transformative commercial value across countless sectors. Gen QAI is a direct result of our full-stack capabilities and our leadership in hybrid classical-quantum computing, delivering an entirely new approach that stands to revolutionize AI." - Dr. Raj Hazra, President and CEO of Quantinuum [24]
Traditional AI models, such as GPT-3, consumed around 1,300 MWh of energy - enough to power 130 U.S. homes. In contrast, Quantinuum's Helios quantum computer used 30,000 times less energy than the Frontier supercomputer for similar tasks [23].
Here’s a quick look at how quantum-enhanced AI stacks up against traditional AI systems:
Aspect | Traditional AI | Quantum-Enhanced AI |
|---|---|---|
Processing Power | Limited by classical bits | Exponentially higher with qubits |
Energy Efficiency | High consumption (e.g., GPT-3: 1,300 MWh) | 30,000x more efficient |
Parameter Requirements | Extensive | Significantly fewer |
Machine Learning Efficiency | Baseline | Up to 1,000x improvement |
ZenaTech Inc. showcased a real-world example by enhancing AI drones with quantum computing for wildfire monitoring on Native American reservations. These drones processed massive datasets that classical systems couldn’t handle.
"The generation of meaningful synthetic data, specifically when you do not have many training data, is nontrivial and we see it as a new era for AI unlocked by quantum technologies." - Dr. Thomas Ehmer, Healthcare business sector of Merck KGaA, Darmstadt, Germany [24]
The global market for quantum AI, valued at $256.0 million in 2023, is expected to grow at a 34.4% annual rate from 2024 to 2030 [26]. This growth is driven by quantum computing’s ability to improve machine learning algorithms and handle previously unmanageable datasets, especially in finance, healthcare, and manufacturing.
This powerful combination of quantum computing and AI is opening doors to even more advancements in quantum technologies.
6. First Working Quantum Network
Quantum networking took a giant step forward in 2025, marking a milestone in the field of quantum computing. This progress built on earlier developments, such as the EPB Quantum Network in Chattanooga, Tennessee - the first commercial quantum network in the U.S. [28].
The game-changer came from Caltech researchers, who created a multi-qubit network using nanofabricated yttrium orthovanadate (YVO4) crystals. These crystals housed around 20 ytterbium atoms per node, allowing quantum information to be transmitted in parallel [27]. This achievement was rooted in earlier breakthroughs in qubit control and stability.
"This is the first-ever demonstration of entanglement multiplexing in a quantum network of individual spin qubits. This method significantly boosts quantum communication rates between nodes, representing a major leap in the field."
– Andrei Faraon, William L. Valentine Professor of Applied Physics and Electrical Engineering at Caltech [27]
This innovation paved the way for further progress. In October 2024, QuTech successfully connected two quantum computers located in different cities. Shortly after, Photonic linked qubits across separate systems, marking another key moment in quantum networking [10].
"General-purpose entanglement-based quantum networks are not a single-purpose solution - these networks are more like the TCP/IP of the quantum world." [28]
The current network architecture combines various qubit technologies - like superconducting qubits, photonic qubits, trapped ions, neutral atoms, and silicon spin qubits - into a cohesive quantum computing framework [29].
In practical applications, the Bank of Communications used quantum key distribution to complete secure transactions between Shanghai and Beijing, showcasing how quantum networks are enhancing financial security [30].
These advancements are laying the groundwork for future innovations in secure communication, distributed computing, and quantum sensing.
7. Chemical Modeling with Quantum Systems
In 2025, advancements in quantum networks and AI brought major changes to chemical modeling. Quantum computing has significantly improved the accuracy and efficiency of molecular simulations. Qunova Computing achieved chemical accuracy with its HiVQE algorithm, cutting computational resource needs by a factor of 1,000 compared to traditional methods [31]. This algorithm has been successfully tested on systems like IQM's 20-qubit setup, IBM's 24-qubit Quantum Eagle processor, and AQT's IBEX Q1 ion-based machine, analyzing molecules such as lithium sulfide, hydrogen sulfide, water, and methane [31].
"We think this method could be a game-changer in terms of understanding complex chemistry and materials science problems. It's a way to study certain phenomena at a much more affordable computational cost."
– Laura Gagliardi, Richard and Kathy Leventhal Professor in UChicago PME and the Department of Chemistry [32]
Terra Quantum and RWTH Aachen University introduced a quantum tensor network approach that speeds up molecular structure determination by 5–20 times. This method has been particularly effective in analyzing complex pharmaceutical compounds like penicillin and ritonavir [35].
"Tensor train optimization for conformer search offers a physics‐driven approach, unlike many machine learning‐based methods that rely on large datasets. Our method finds highly accurate conformers with significantly fewer function evaluations than competing optimization techniques, delivering substantial speed‐ups and a data‐independent solution."
– Dr. Roman Ellerbrock, Head of Applied Research in Chemistry, Terra Quantum [35]
Quantum technology is also reshaping pharmaceuticals. Pfizer, in partnership with IBM's Quantum Network, is accelerating the search for new antibiotics and antivirals. Meanwhile, Google's quantum division is modeling cancer-related protein structures [33]. Considering that traditional drug development costs range from $1–2 billion per approved drug [35], these advancements could lead to major cost reductions.
In another area, NOVONIX and SandboxAQ are using quantum-powered software to dramatically shorten battery cell prototyping and testing times - from years to just weeks [34].
Finally, the multiconfiguration pair-density functional theory (MC-PDFT) combined with the new MC23 functional is delivering highly precise electron correlation analysis. This approach offers better accuracy than traditional methods while consuming far less power [32].
8. Quantum-Ready Security Systems
As quantum computing progresses, protecting its applications becomes increasingly critical. By 2025, quantum-ready security systems are addressing these challenges, with 50% of federal IT leaders working on quantum-resistant infrastructure strategies and 35% allocating plans and budgets for quantum readiness [36].
Futurex's CryptoHub platform supports NIST-approved post-quantum cryptography (PQC) algorithms like Kyber, Dilithium, and SPHINCS+, enabling smooth integration of quantum-safe encryption [36].
"With finalized NIST PQC standards, agencies must accelerate their migration efforts. By developing flexible and scalable strategies today, they will be prepared to modernize and build long-term resilience against emerging quantum threats." - Ben Gianni, senior vice president and CTO of GDIT [36]
Currently, 75% of encryption methods are vulnerable to quantum attacks [39]. The U.S. government aims for a full transition to PQC by 2030 (or 2035, as outlined in National Security Memorandum 10), with an estimated transition cost of $7.1 billion [3][38].
Key security features are evolving to meet quantum challenges:
Security Aspect | Traditional Systems | Quantum-Ready Systems |
|---|---|---|
Key Generation | Pseudo-random numbers | Quantum randomness |
Attack Resistance | Vulnerable to quantum | Resistant to both classical and quantum |
Implementation Cost | Lower, mature technology | Higher, requires new infrastructure |
Detection Capability | May miss intrusions | Detects disturbances in quantum states |
"As organizations begin the transition to post-quantum cryptography over the next year, agility will be crucial to ensure systems are prepared for continued transformation, particularly as the NIST continues to expand its toolbox of post-quantum cryptography standards." - Ray Harishankar, IBM fellow at IBM Quantum Safe [3]
Practical examples of quantum security are already emerging. BT and Toshiba have implemented a quantum key distribution network in the UK, enabling secure data transmission [37]. Meanwhile, China has developed a large-scale quantum-secure network connecting multiple cities [37].
The demand for quantum computing security solutions is expected to grow by 31% annually through 2030 [39]. Additionally, 95% of global executives view next-generation computing as a major driver for the decade ahead [39]. These advancements highlight the rapid evolution of quantum security technologies.
9. Advances in Quantum Measurement
Quantum measurement technology reached new heights in 2025. DARPA's INSPIRED program introduced squeezed light sources that cut quantum noise by 40 times, significantly boosting the accuracy of optical detection systems [40].
In January 2025, researchers at the University of Pennsylvania used diamond nitrogen-vacancy centers to detect Nuclear Quadrupole Resonance (NQR) signals from individual atoms, uncovering molecular details that were previously undetectable.
"This technique allows us to isolate individual nuclei and reveal tiny differences in what were thought to be identical molecules. By focusing on a single nucleus, we can uncover details about molecular structure and dynamics that were previously hidden. This capability allows us to study the building blocks of the natural world at an entirely new scale."
– Lee Bassett, Associate Professor and Director of Penn's Quantum Engineering Laboratory [41][42]
These breakthroughs are already making an impact across several fields:
Application Area | Innovation | Impact |
|---|---|---|
Healthcare | Optically Pumped Magnetometers | Portable diagnostics with room-temperature operation [43] |
Defense | RoQS Program | Quantum sensors resistant to environmental interference [45] |
Research | Nanodiamond Microdroplets | Trace ion and molecule detection using just 63¢ worth of diamond dust per analysis [46] |
At UC Berkeley and Berkeley Lab, scientists demonstrated a new method using nanodiamonds in microdroplets for quantum sensing. This technique successfully detected small amounts of gadolinium ions and TEMPOL, delivering high performance with minimal sample sizes [46].
"You can envision setting up bioreactors in austere environments around the world or in space, to make things like food that you couldn't deliver on a daily basis. Having precise quantum sensors that tell you how the microorganism culture is behaving is an important step toward that dream. To build a self-regulating bioreactor, we need that real-time intracellular data."
– Deepti Tanjore, Director of the Advanced Biofuels and Bioproducts Process Development Unit at Berkeley Lab [46]
The Pentagon has invested $100 million in quantum technologies for positioning and timing, emphasizing their strategic importance [44]. These applications range from fetal magnetocardiography for monitoring heart rhythms to diamond-based sensors capable of measuring cellular-level temperature and magnetic fields [43].
"We weren't even sure whether our technique would work, but it turned out to be surprisingly easy and effective."
– Ashok Ajoy, Faculty Scientist at Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory [46]
These advancements are transforming quantum measurement into one of the most refined quantum technologies available today. They are reducing costs and improving precision, paving the way for further progress in measurement, detection, and even the next steps in quantum computing.
10. Public Access to Quantum Computing
In 2025, quantum computing became more accessible than ever, thanks to major cloud providers offering these systems to businesses and researchers worldwide. This shift eliminated the need for costly hardware investments and opened up new possibilities for innovation.
Here are three key cloud platforms leading the charge in making quantum computing more accessible:
Platform | Key Features | Notable Applications |
|---|---|---|
Amazon Braket | Access to superconducting, trapped ion, and neutral atom devices | Automotive process optimization |
Microsoft Azure Quantum | Includes Q# programming, Quantum Development Kit, and HPC cluster integration | Scientific simulations and molecular modeling |
IBM Qiskit | Open-source framework with cloud-based quantum processors | Research, development, and education initiatives |
This accessibility is already delivering results across various industries. For example, Volkswagen used Amazon Braket to optimize its binary paint shop, while BMW Group collaborated with the Amazon Quantum Solutions Lab to drive advancements in automotive technology [48].
"Cloud-centric quantum computing will democratize access to quantum power, enabling organizations to solve complex problems more efficiently and cost-effectively." – Jorge Alberto Hernández C. [47]
The market reflects this growing interest: the global quantum computing sector is projected to hit $1.238 billion by 2025, with a CAGR of 31.2%, reaching $8.2856 billion by 2032 [49]. Quantum cloud applications are already transforming industries:
Industry | Quantum Cloud Applications | Impact |
|---|---|---|
Financial Services | Portfolio optimization and fraud detection | Better risk management and security |
Healthcare | Molecular modeling and drug discovery | Faster research and development |
Logistics | Route optimization and supply chain management | Greater operational efficiency |
Smart Cities | Traffic flow optimization and IoT integration | Real-time urban solutions |
Quantum computing is also enhancing smart city systems, enabling real-time management through IoT applications and natural language processing [50].
Conclusion
The advancements highlighted for 2025 mark a turning point for quantum computing. With the global quantum computing market expected to hit $928.8 million by the end of 2025 and grow to $6.5 billion by 2030 [52], the field is poised for exponential growth.
Key developments, such as AWS's Ocelot chip, which slashes quantum error correction costs by 90%, and steady progress in qubit stability, are addressing long-standing challenges like ensuring reliable qubit operations [22]. These strides are critical for the technology's practical application.
Quantum computing's impact on cybersecurity is also becoming increasingly clear. Gartner warns that by 2029, most conventional asymmetric cryptography could be compromised by quantum advancements [51]. This poses serious economic risks, with potential global GDP losses estimated between $2 trillion and $3.3 trillion due to quantum-related security breaches.
"There are still significant hurdles before we reach the day when quantum computers are able to break classical encryption. According to the majority of scientists and academics, we are still about five to 10 years away from such an event."
– Duncan Jones, head of cybersecurity, Quantinuum [51]
The intersection of quantum computing and AI is another transformative area. Dr. Ahmet Erdemir explains:
"AI methods are currently limited by the abilities of classical computers to process complex data. Quantum computing can potentially enhance AI's capabilities by removing the limitations of data size, complexity, and the speed of problem solving" [25]
Despite these advancements, scalability and error correction remain pressing challenges. Oskar Painter offers a realistic perspective:
"I think somewhere in between 10 and 20 years, I have some good confidence that we'll have practical, useful quantum computers in that timeframe. But we also need to take a sort of humble and realistic approach to the work we have to do going forward" [1]
Quantum optimization is quickly becoming a game-changer for businesses. Dr. Alan Baratz highlights its importance:
"Quantum optimization will emerge as the killer use case for quantum computing, becoming an operational necessity for businesses looking for novel strategies to maintain competitiveness" [53]
As technical progress aligns with business needs, organizations must act now to prepare for a quantum-driven future. The National Security Memorandum 10 underscores this urgency, setting a 2035 deadline for migrating to post-quantum cryptography [3]. These developments not only showcase the achievements of 2025 but also align with the larger goals set earlier this year.






